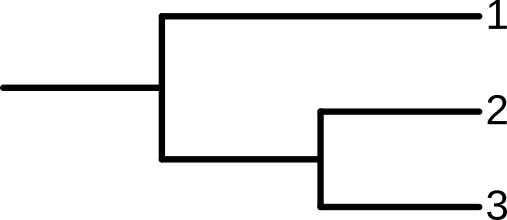
What is a phylogeny?
What are phylogenies?
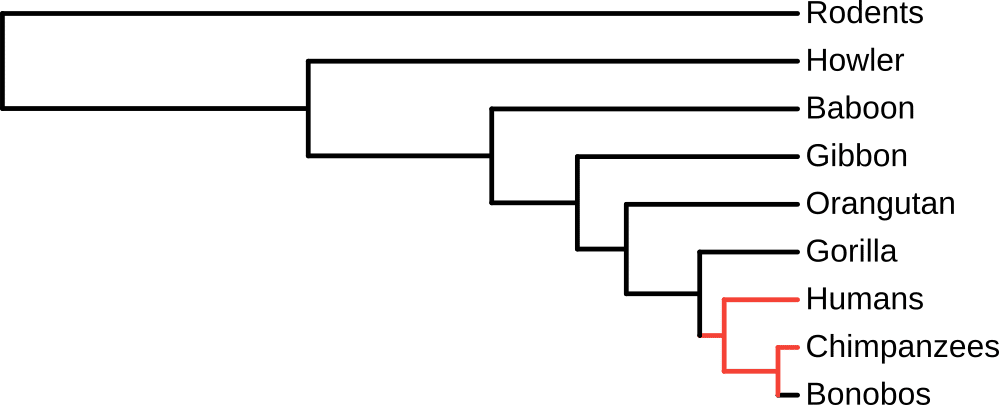
A phylogenetic tree (otherwise known as a phylogeny) is a graphical representation of evolutionary relationships. At its most basic level, a phylogeny tells us how units of life such as species, individuals, or genes are related to one another.
For example, on this phylogeny we can tell humans are related to chimpanzees because of how the lines (highlighted in red) connect the 2 species.
Most modern phylogenies are based on genetic information. Lets make a simplified example with 3 species we want to build a phylogeny for based on the following genetic sequences.

Looking at the sequences, we can visually see that 1 is not at all similar to 2 or 3. In fact, sequence 1 only shares information with sequences 2 and 3 at the second to last nucleotide (All A)!
But, we can see that sequence B is really similar to sequence C. They only differ by a single nucleotide (the 4th nucleotide is G for sequence 2, but T for sequence 3)!
We can use a phylogeny to show how these sequences are related to one another. Where sequences 2 and 3 are connected to one another, before they are connected to sequence 1.