What are sister groups?
Sister groups are when two tips or clades share an immediate internal node (MRCA). They are each others closest living relatives. Sister species specifically refer to tips who are each others closest living relative. Lets take a look look at apes!
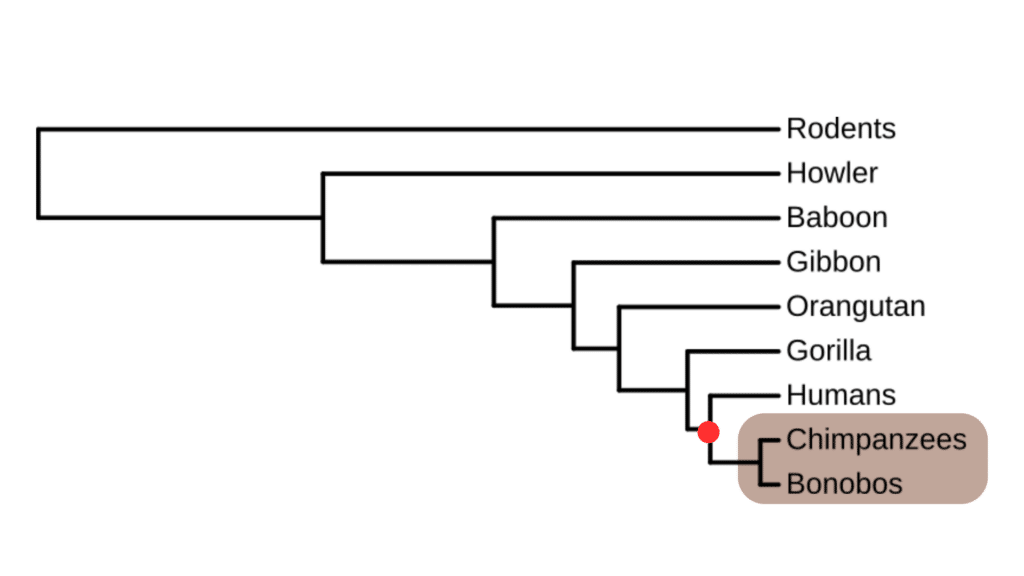
Here the Bonobo and the Chimpanzee are sister species to one another. They are each others closest living relative represented by the Most Recent Common Ancestor at the node highlighted in red. For example, Chimpanzees and Orangutans are not sister species as there are other species of organisms more closely related to each group on our phylogeny.
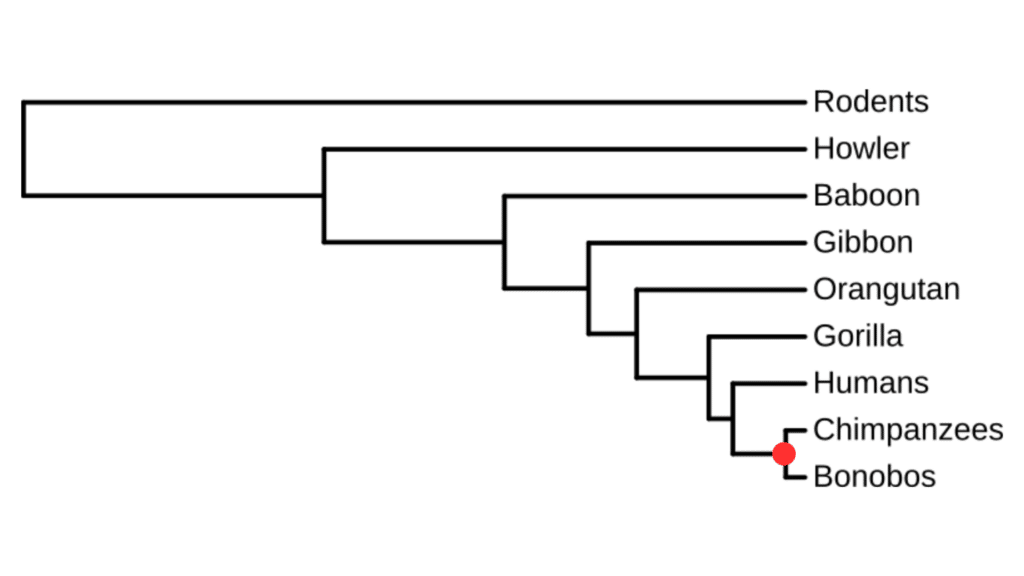
But we can also use entire groups of species, so called sister groups! For example, what is the sister species to humans? We could say either the Chimpanzees or the Bonobos are sister to humans, as each are separated from humans by 6 million years of evolutionary history (see adding branch lengths lesson) and are joined to us by the same most recent common ancestor (red in phylogeny below). However, as our phylogeny contains both chimpanzees and bonobos, is it more correct to say the group containing chimpanzees and bonobos is sister to humans. As chimpanzees and bonobos are in the genus Pan, you could also say that Pan is sister to humans. This group is highlighted on the below phylogeny.